Dieldrin in eggs of herring gulls from the North and the Baltic Sea
Significant decrease in contamination of eggs from the North Sea
Dieldrin is a very effective insecticide. It is highly persistent under environmental conditions and has a high potential for bioaccumulation and biomagnification.
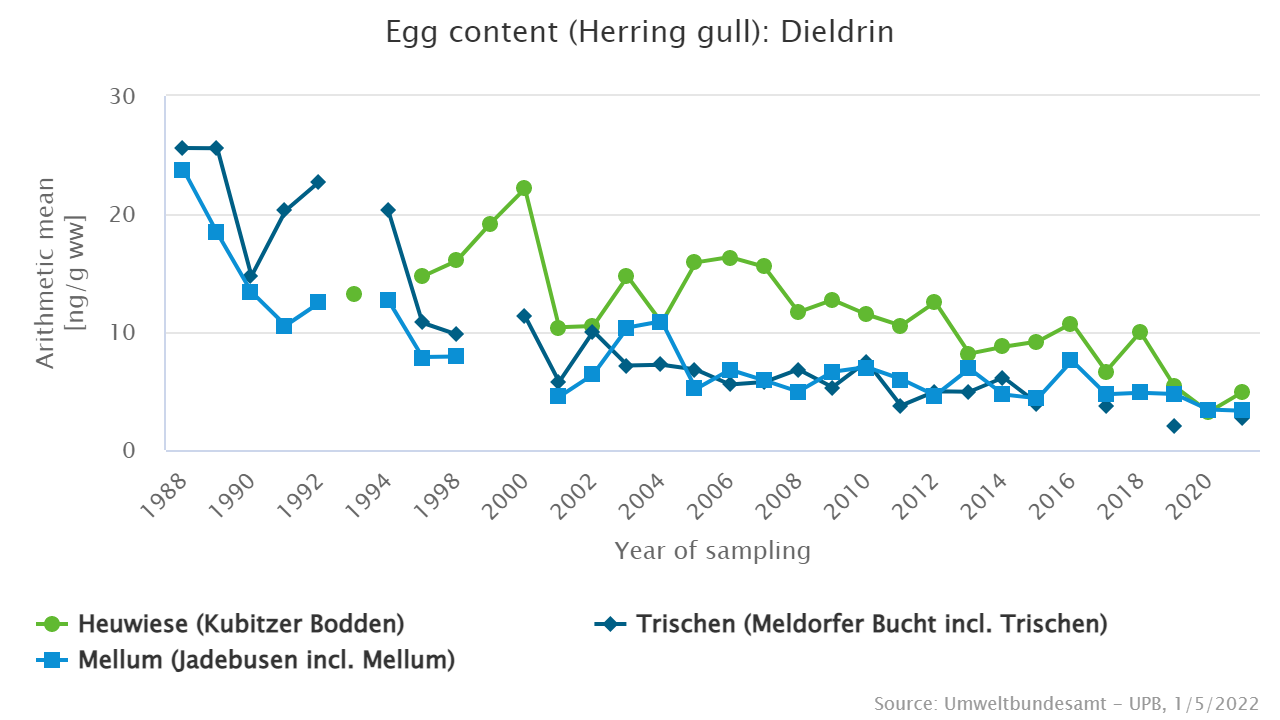
At the end of the 1980s, dieldrin was relatively high in herring gull eggs from the North Sea islands Trischen and Mellum with higher contamination at Trischen. Since then dieldrin concentrations have decreased significantly at both sampling sites and are close to or below the detection limit for several years now. No comparable trend is observed in eggs from the Baltic Sea island Heuwiese. These differences between the North and the Baltic Sea are probably related to differences in pesticide regulation between the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) and the former German Democratic Republic (GDR): whereas dieldrin was banned in the FRG already the early 1970s, it was applied for several more years in the GDR.
Updated at: 2022-01-11
Recommended profiles
Specimen
-
Inshore, the herring gull mainly feeds from the sea: upon fish, mussels, and crabs.
Analytes
-
Very effective insecticide that was widely used as contact and stomach poison for soil insects like termites, grasshoppers and beetles and for textile pests until the early 1970s
Sampling area
-
National Park in the largest brackish water (Bodden) habitat of the world.
-
National park in the world largest connected sand and mud flats.